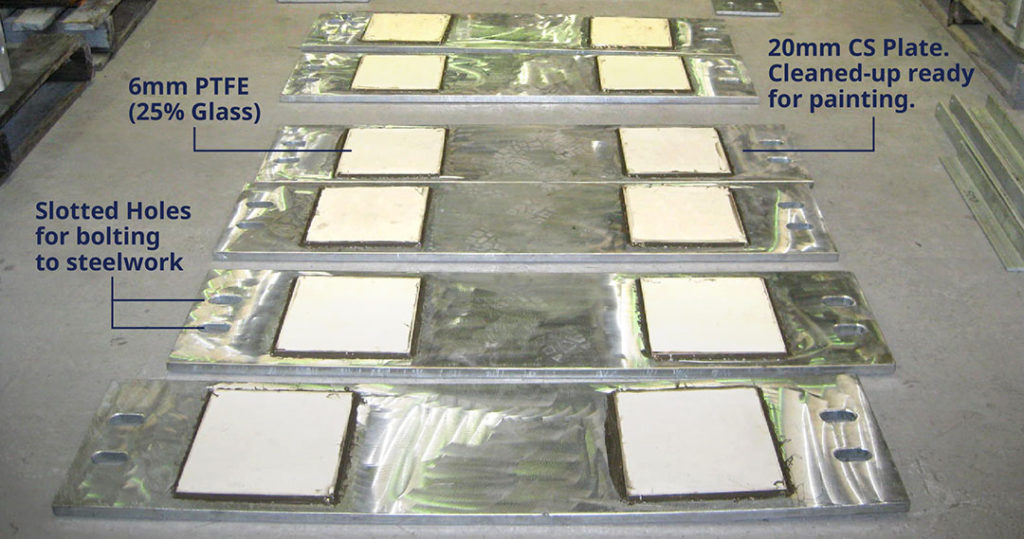
- Products
-
-
-
Categories
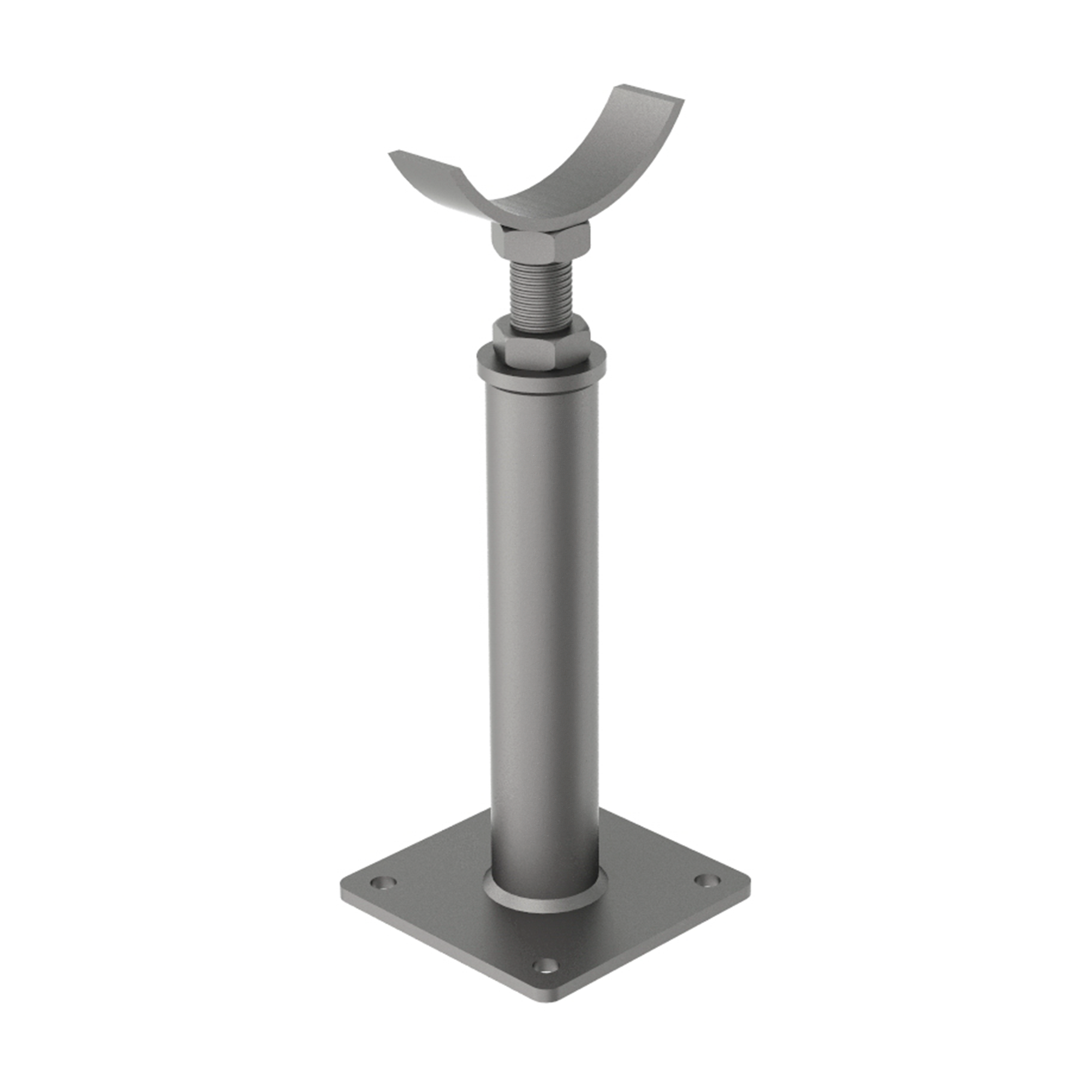
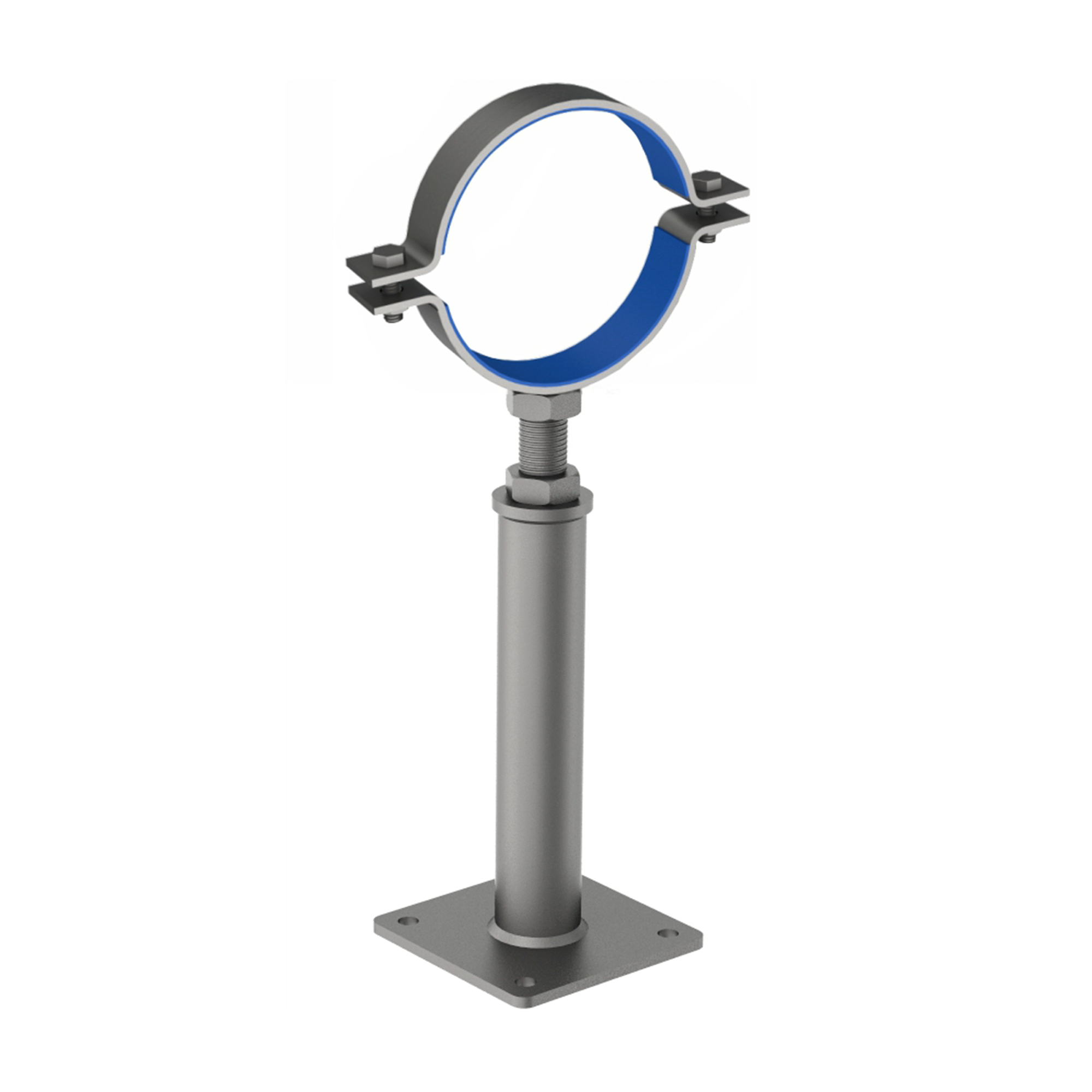
 AG630
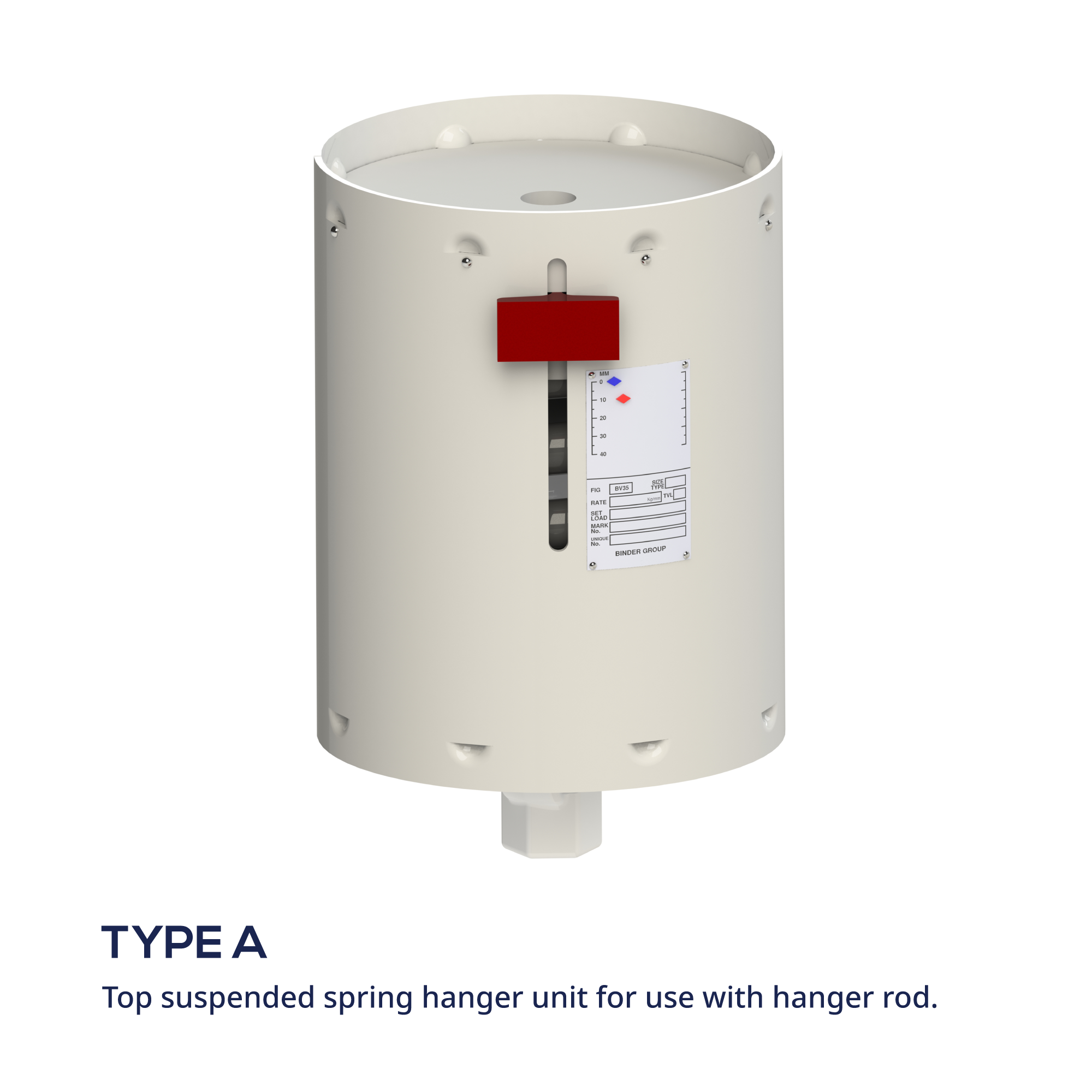
AG630HEIGHT ADJUSTABLE SUPPORT - CRADLE MOUNT
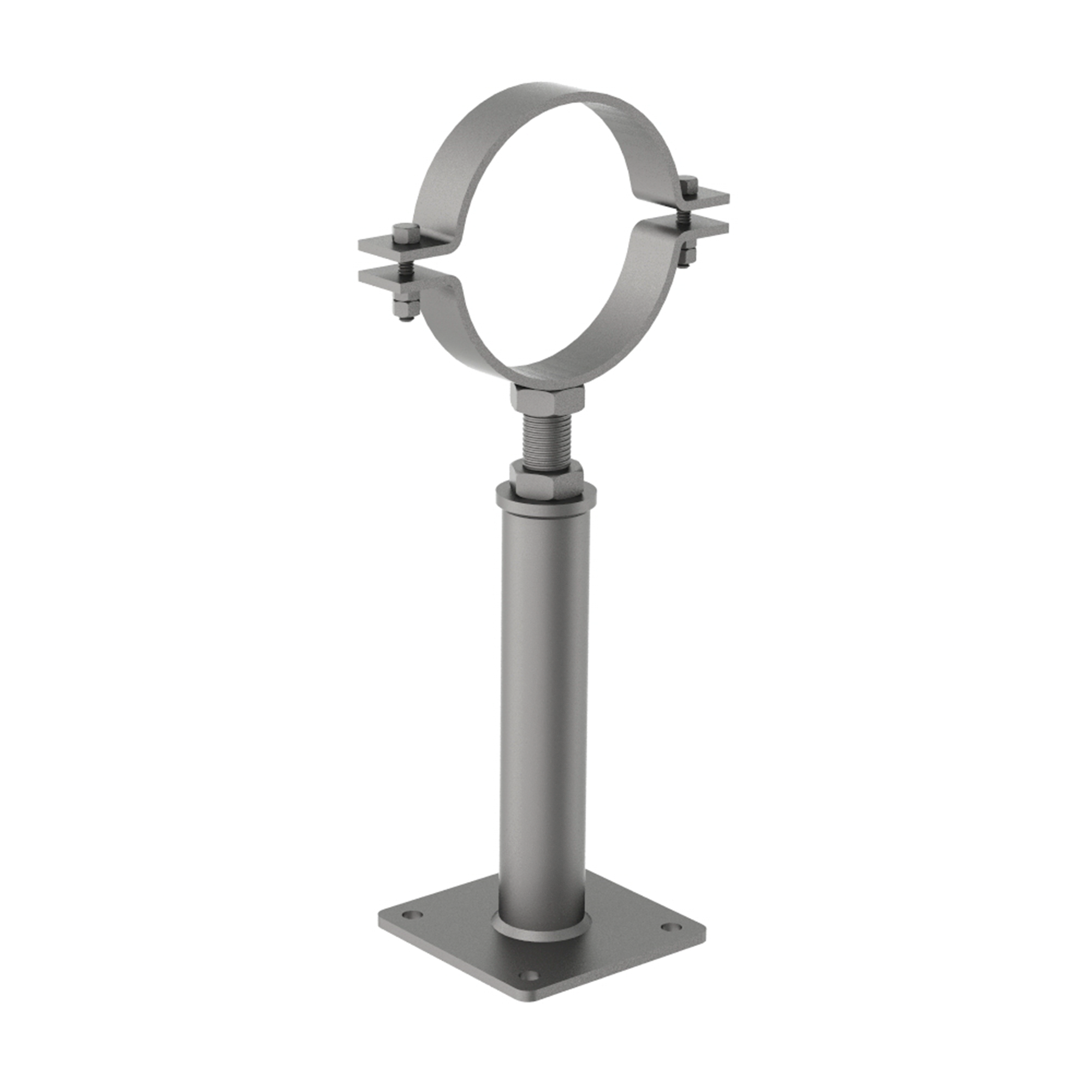
 AG631
AG631HEIGHT ADJUSTABLE SUPPORT - CLAMP MOUNT
 AG632
AG632HEIGHT ADJUSTABLE FLANGE MOUNT
 AG634
AG634INSULATED HEIGHT ADJUSTABLE SUPPORT - CRADLE MOUNT
 AG636
AG636INSULATED HEIGHT ADJUSTABLE SUPPORT - CLAMP MOUNT
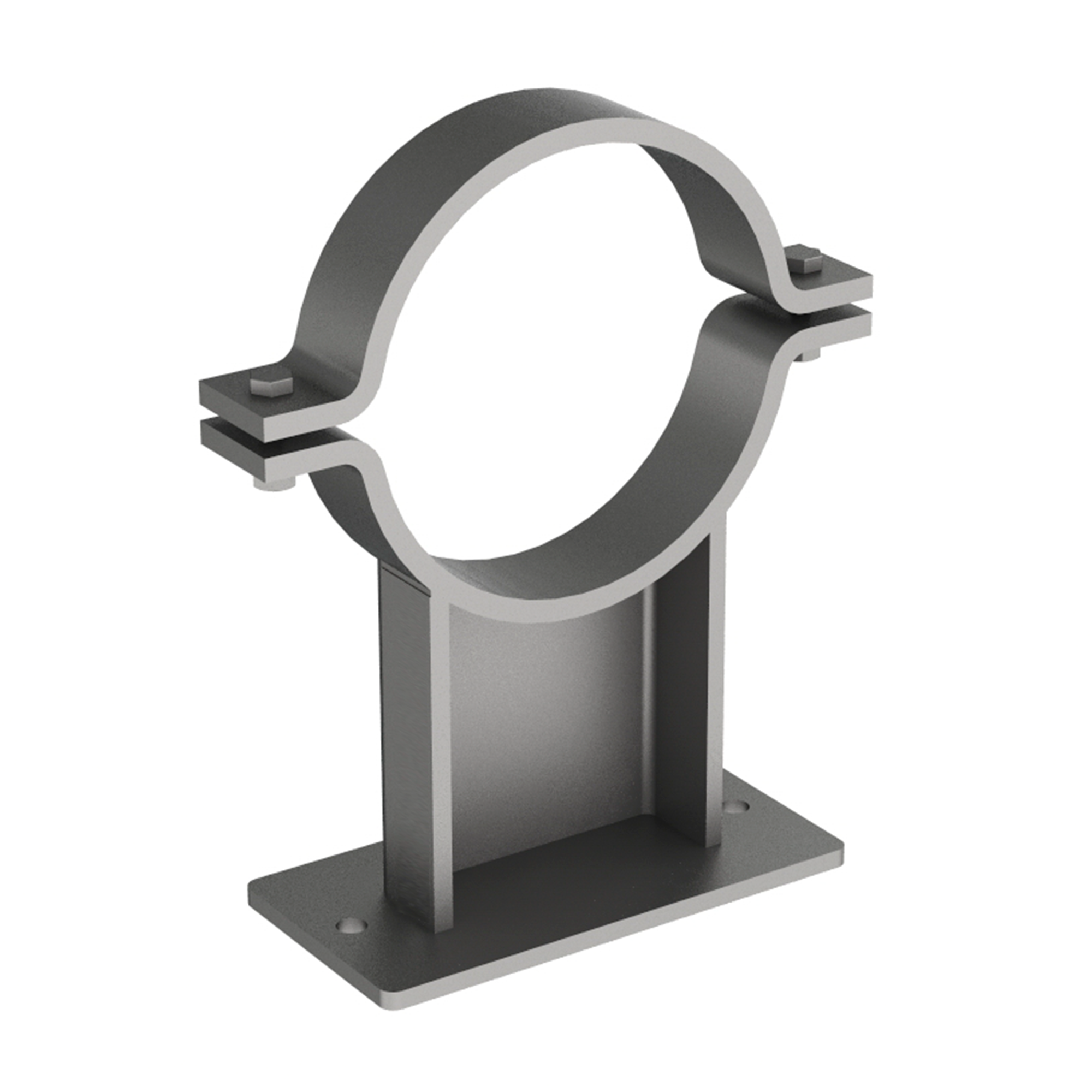
 AG100
AG100LIGHT DUTY 2-BOLT PIPE CLAMP
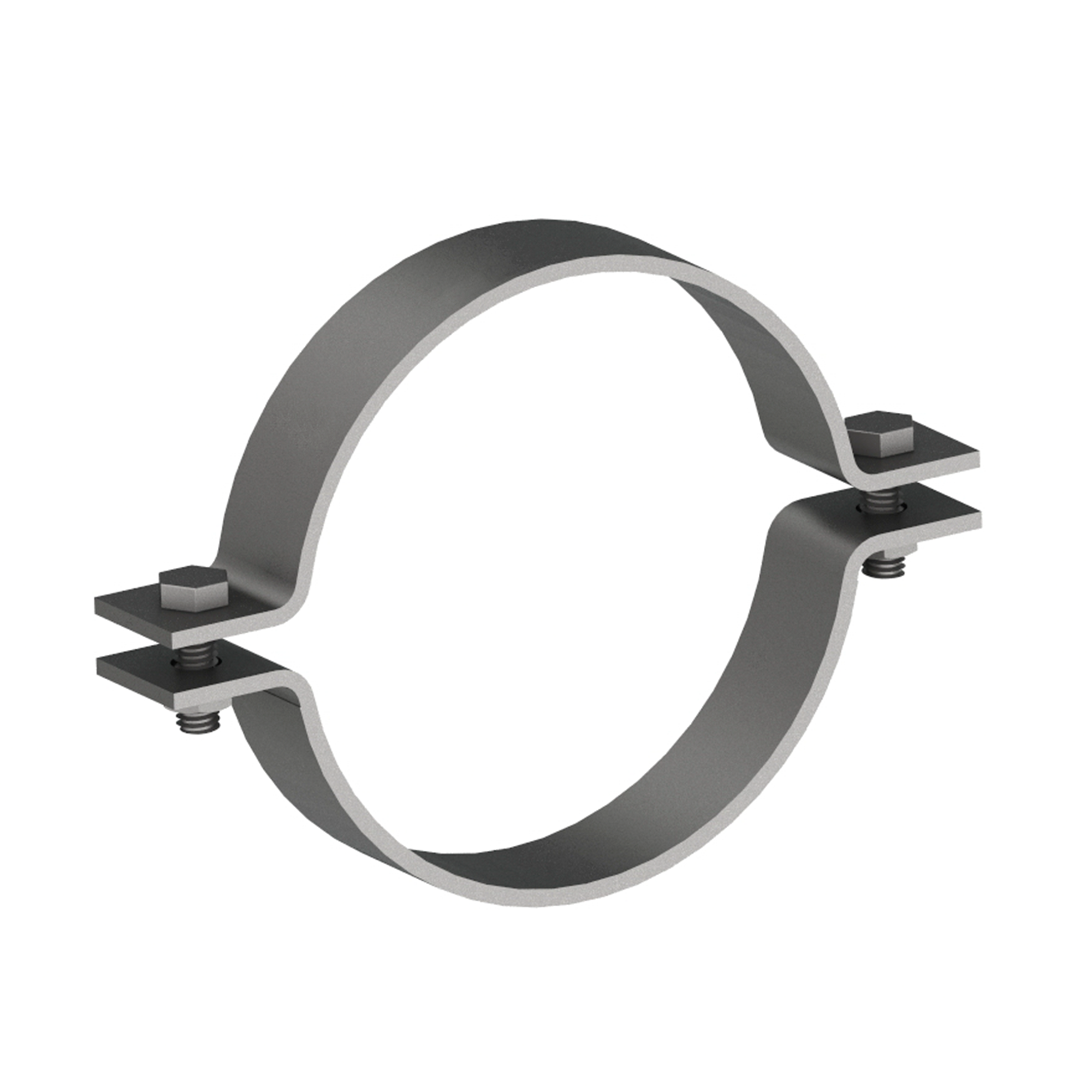
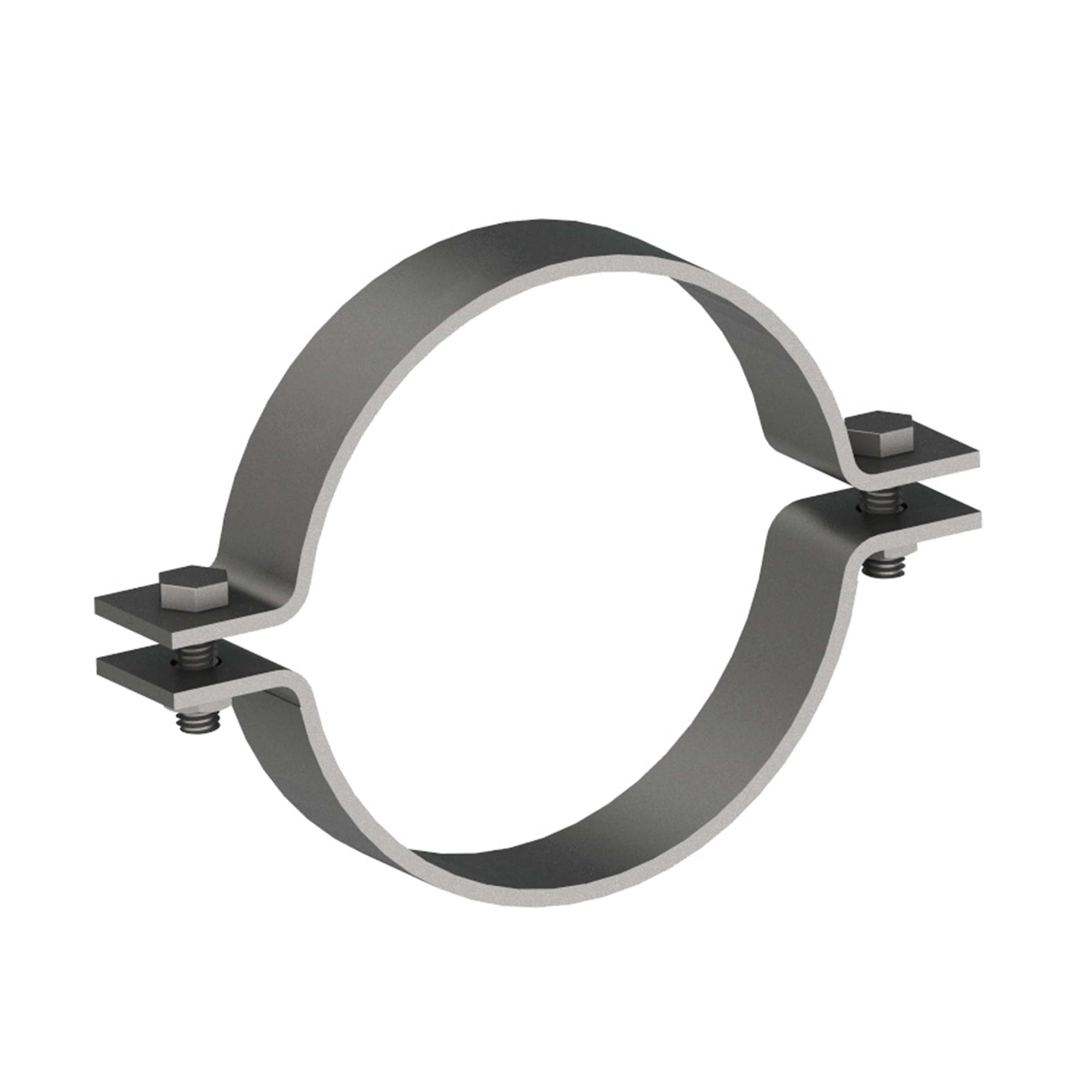
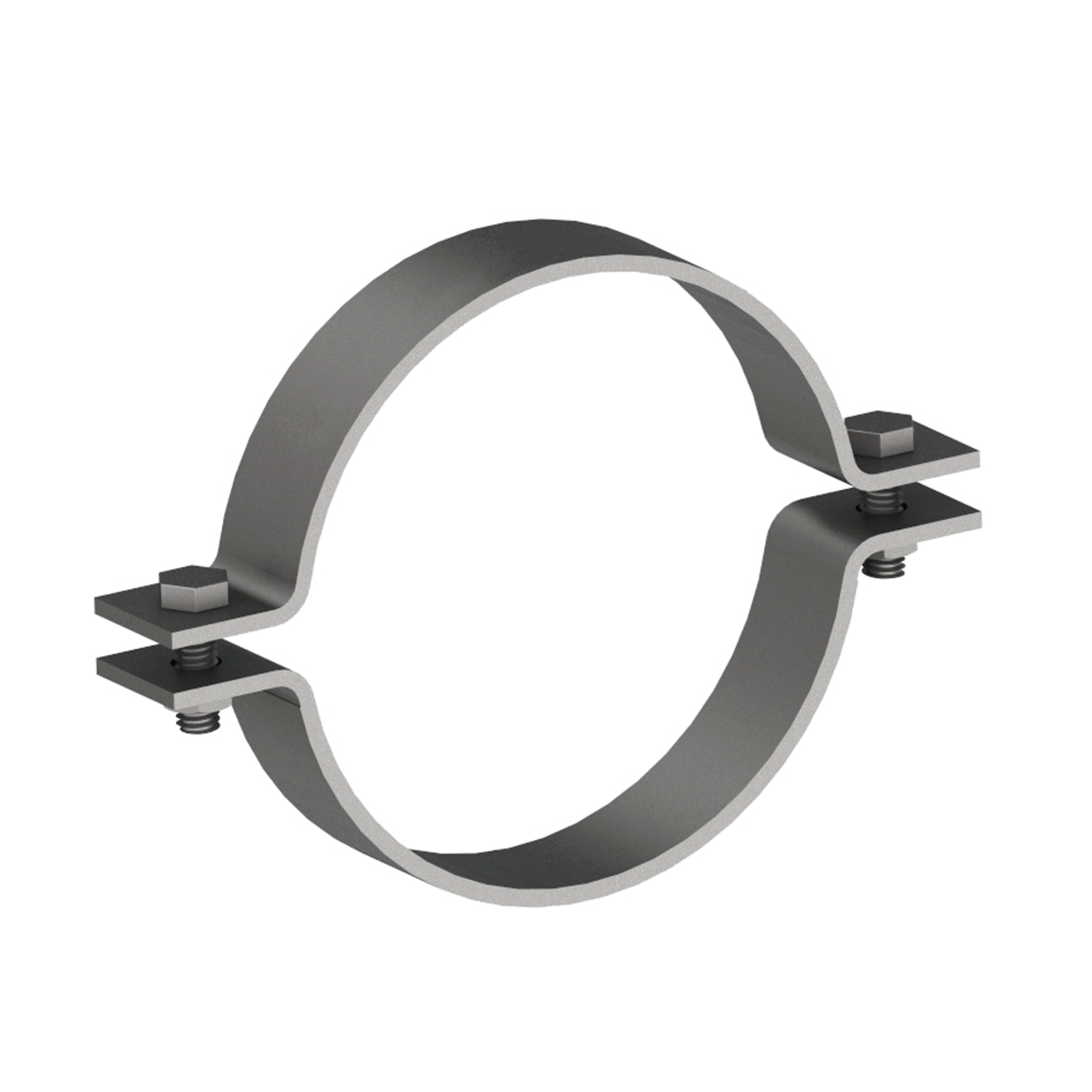
 AG110
AG110MEDIUM DUTY 2-BOLT PIPE CLAMP
 AG112
AG1122-BOLT CLAMP FOR DICL PIPE
 AG115
AG1152-BOLT CLAMP FOR HDPE PIPE
 AG120
AG120HEAVY DUTY 2-BOLT PIPE CLAMP
 AG130
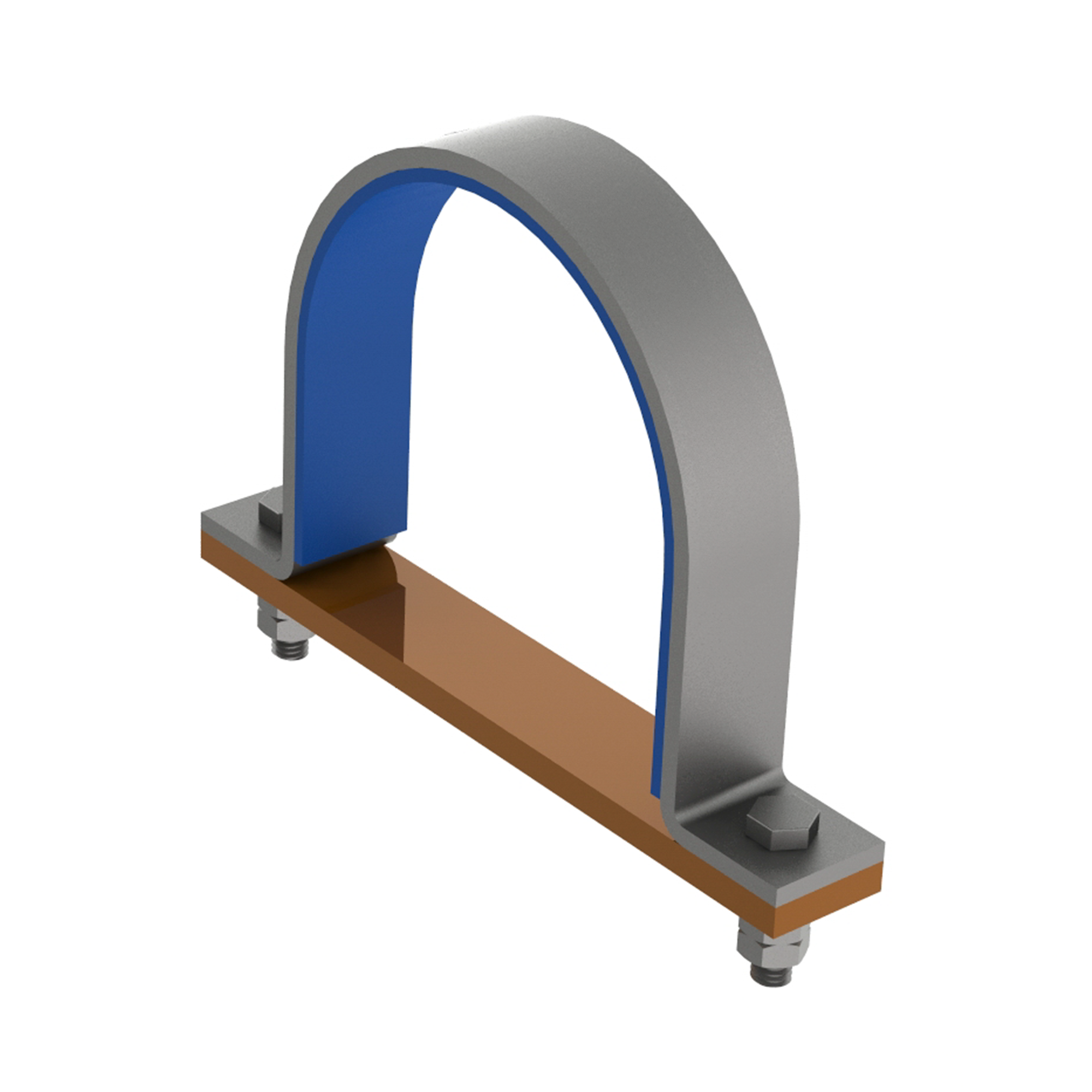
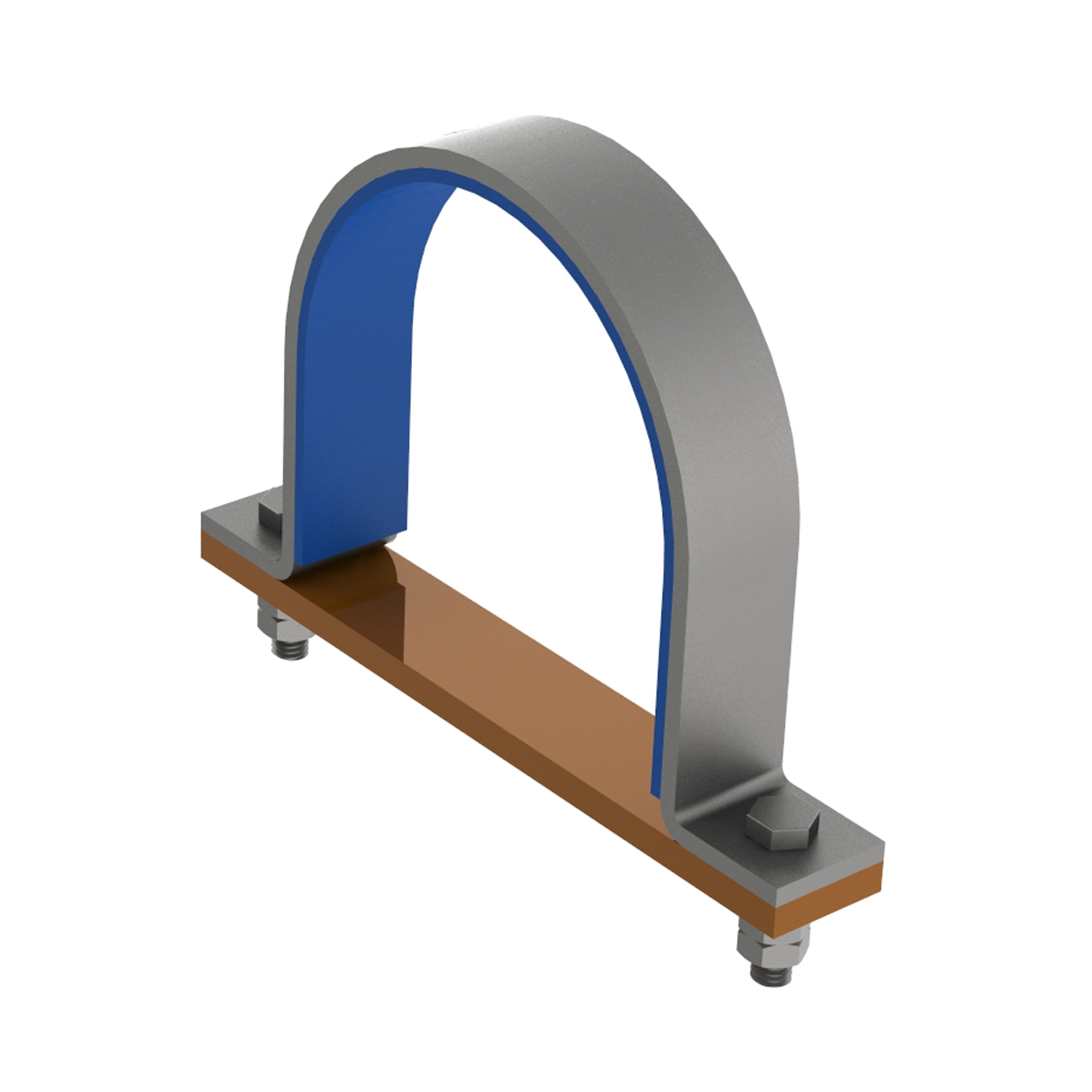
AG130INSULATED 2-BOLT PIPE CLAMP
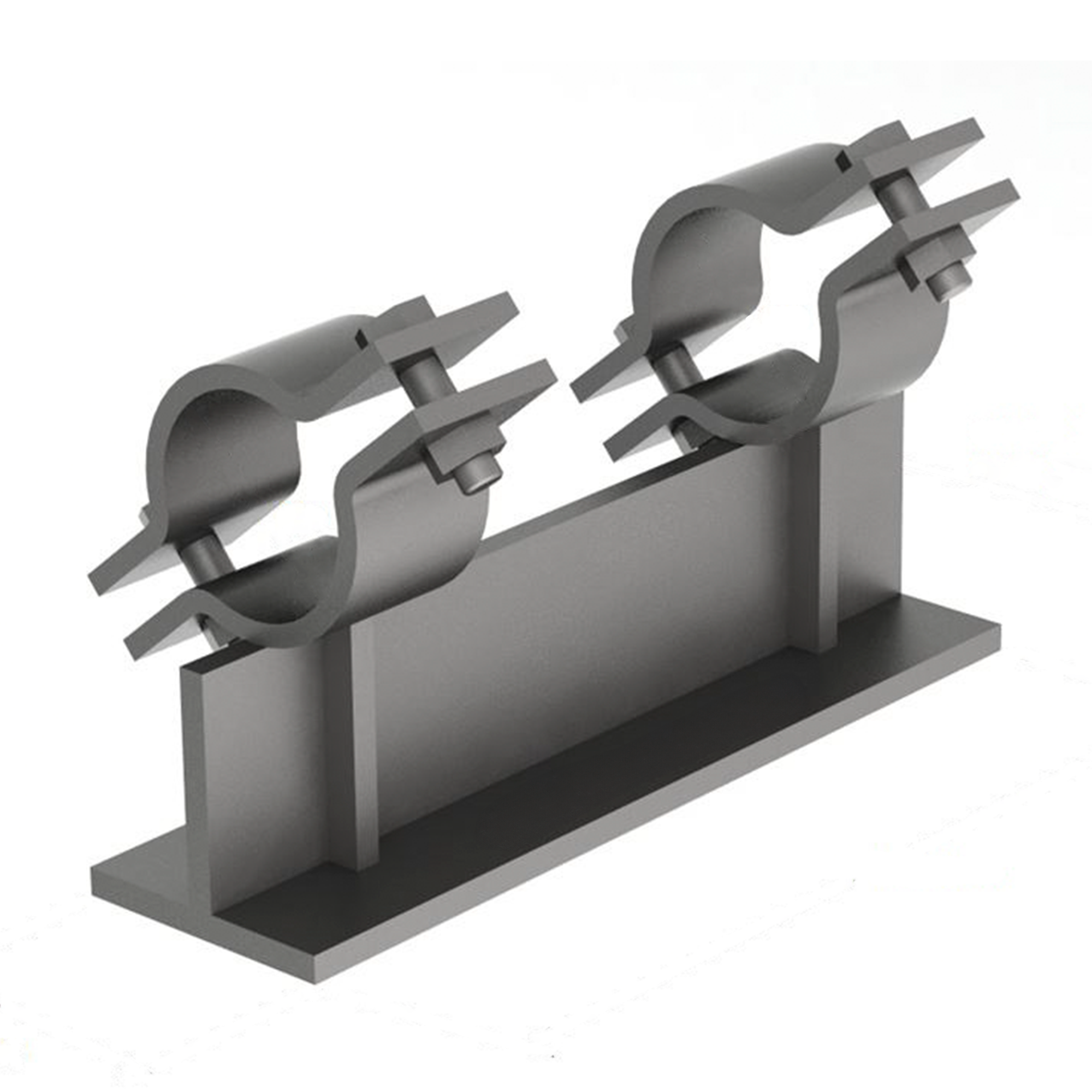
 AG150
AG150LIGHT DUTY 3-BOLT PIPE CLAMP
 AG160
AG160MEDIUM DUTY 3-BOLT PIPE CLAMP
 AG170
AG170HEAVY DUTY 3-BOLT PIPE CLAMP
 AG190
AG1903-BOLT PIPE CLAMP FOR HIGH TEMPERATURES
 AG200
AG200INSULATED 3-BOLT PIPE CLAMP
 AG220
AG220LOW TEMPERATURE RISER SUPPORT
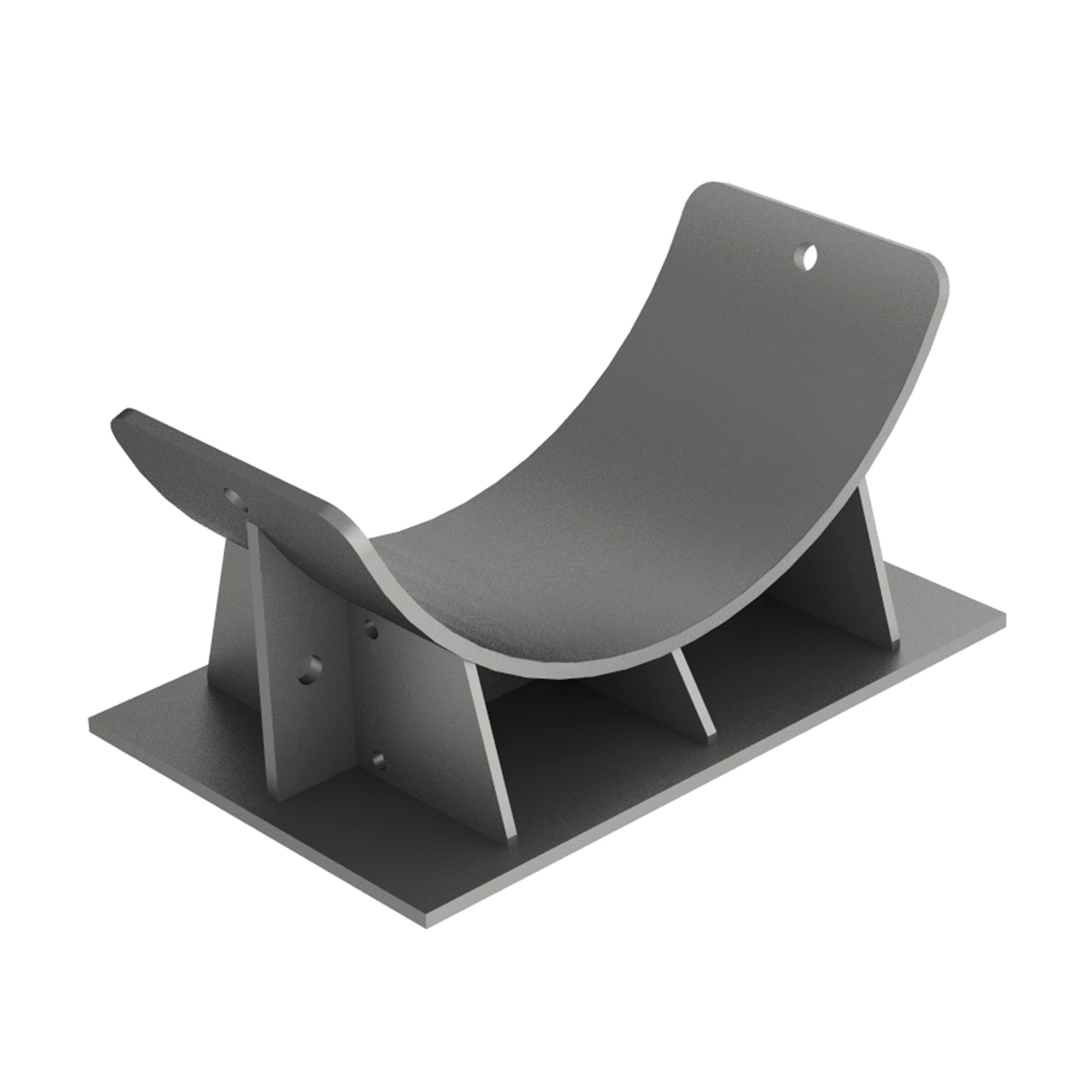
 AG250
AG250CLEVIS CLAMP
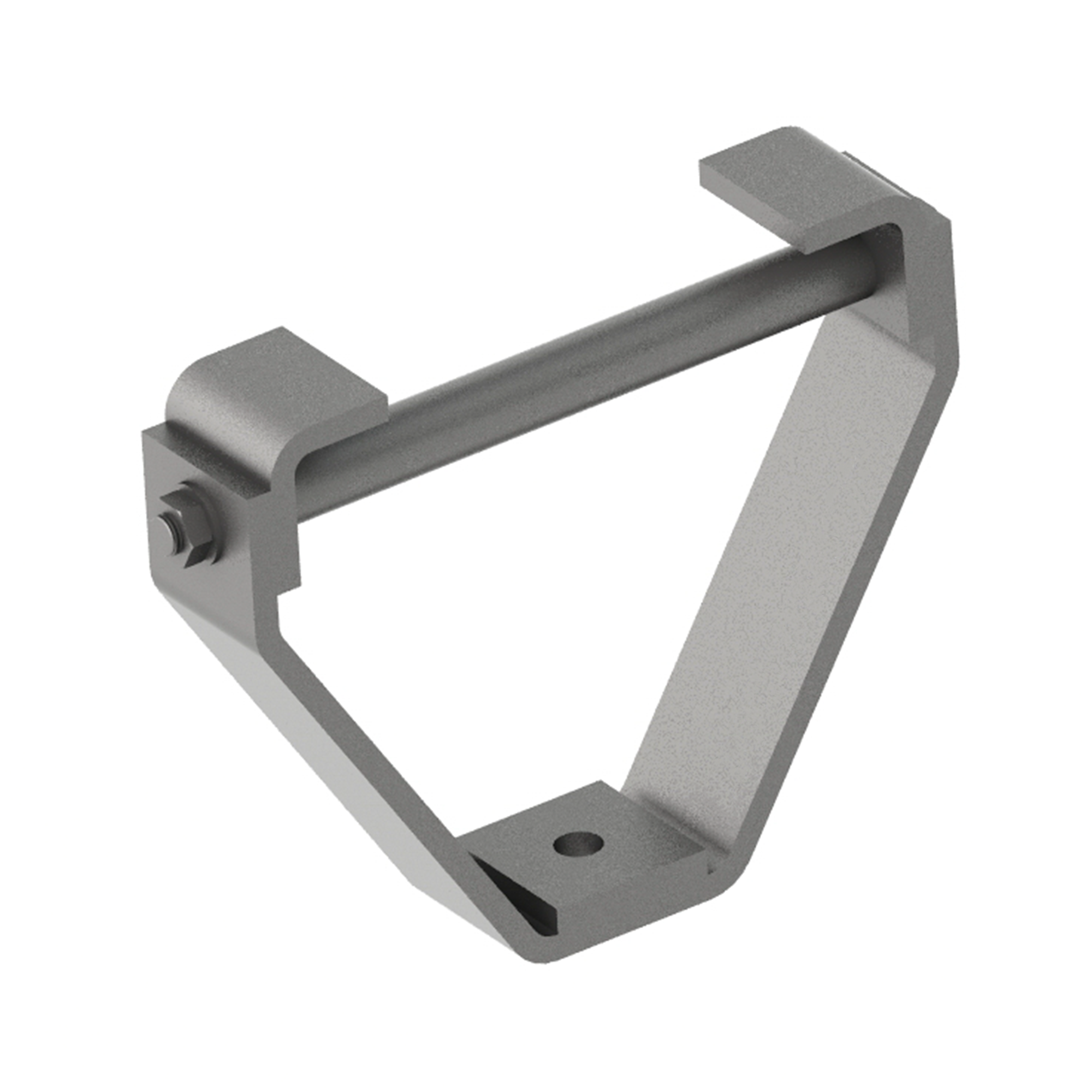
 AG260
AG260BEAM CLAMP
 AG550
AG550HEAVY DUTY PIPE CRADLE
 AG560
AG560CLAMPED PIPE SHOE
 AG565
AG565SINGLE PIPE SHOE
 AG570
AG570DOUBLE PIPE SHOE
 AG580
AG580WELD-ON PIPE SHOE
 AG585
AG585INSULATED SINGLE PIPE SHOE
 AG590
AG590INSULATED DOUBLE PIPE SHOE
 AG595
AG595INSULATED CLAMPED PIPE SHOE AG595
 AG620
AG620SLIDE PLATE
 AG412
AG412SADDLE CLAMP FOR DICL PIPE
 AG415
AG415SADDLE CLAMP FOR HDPE PIPE
 AG420
AG420SADDLE GUIDE
 AG430
AG430SADDLE CLAMP
 AG435
AG435EXTRA HEAVY DUTY SADDLE CLAMP
 AG440
AG440INSULATED SADDLE CLAMP
 AG445
AG445INSULATED SADDLE GUIDE
 AG470
AG470U-BOLT PIPE GUIDE
 AG475
AG475U-BOLT GUIDE FOR HDPE PIPE
 AG480
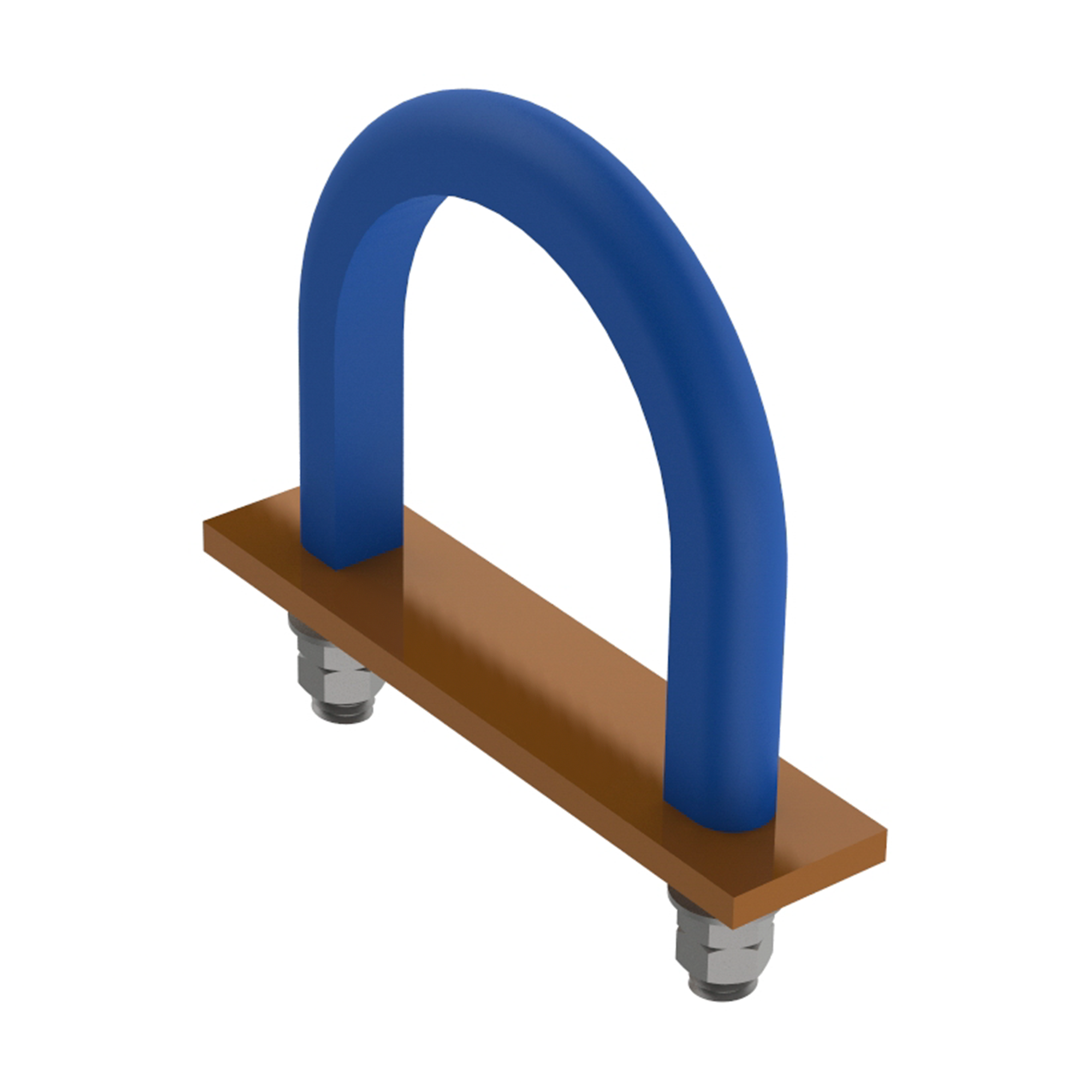
AG480U-BOLT PIPE CLAMP
 AG485
AG485U-BOLT CLAMP FOR HDPE PIPE
 AG490
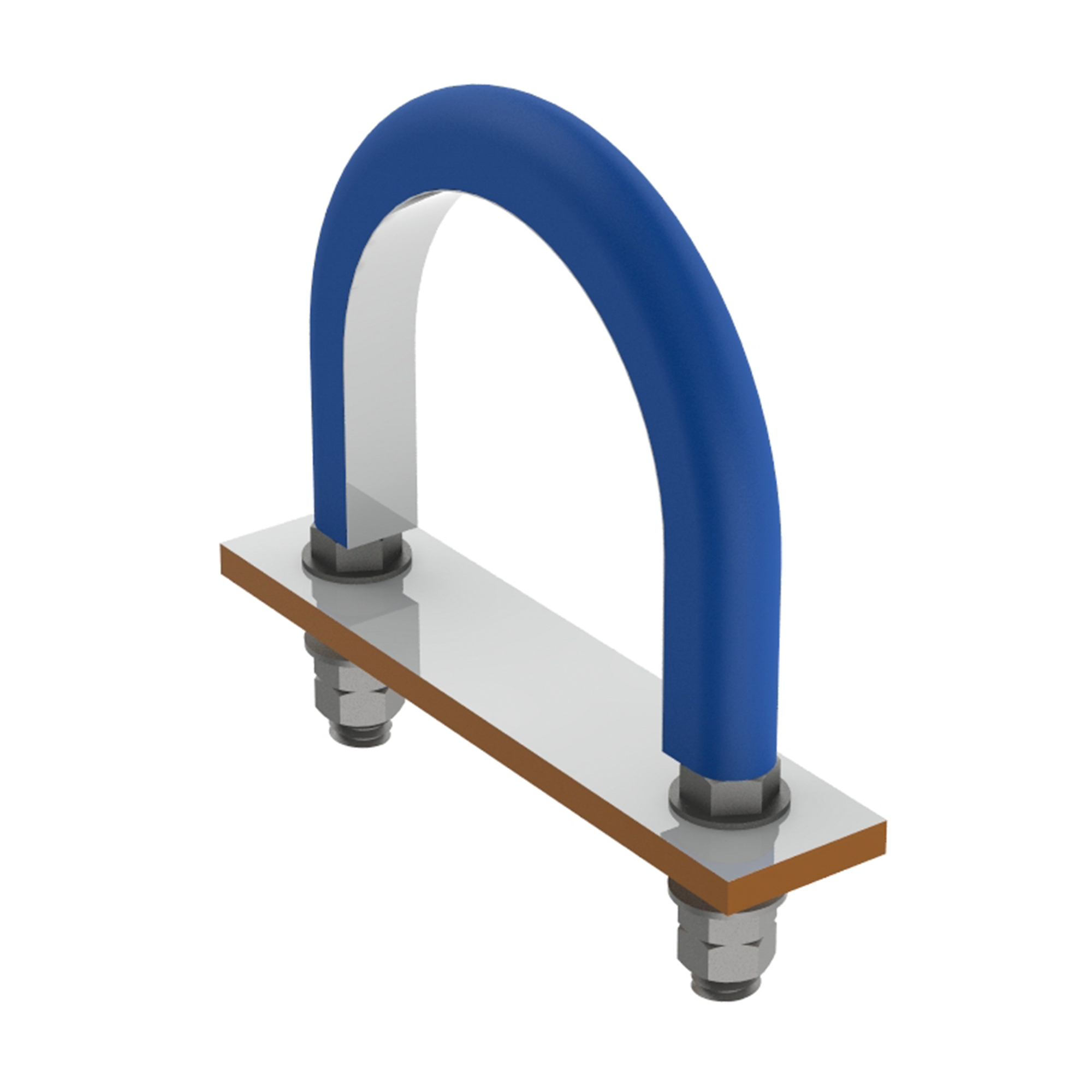
AG490INSULATED U-BOLT PIPE CLAMP
 AG495
AG495INSULATED U-BOLT CLAMP FOR HDPE PIPE
 AG510
AG510INSULATED U-BOLT GUIDE
 AG515
AG515INSULATED U-BOLT GUIDE FOR HDPE PIPE
 AG530
AG530TEFLON INSULATED U-BOLT GUIDE
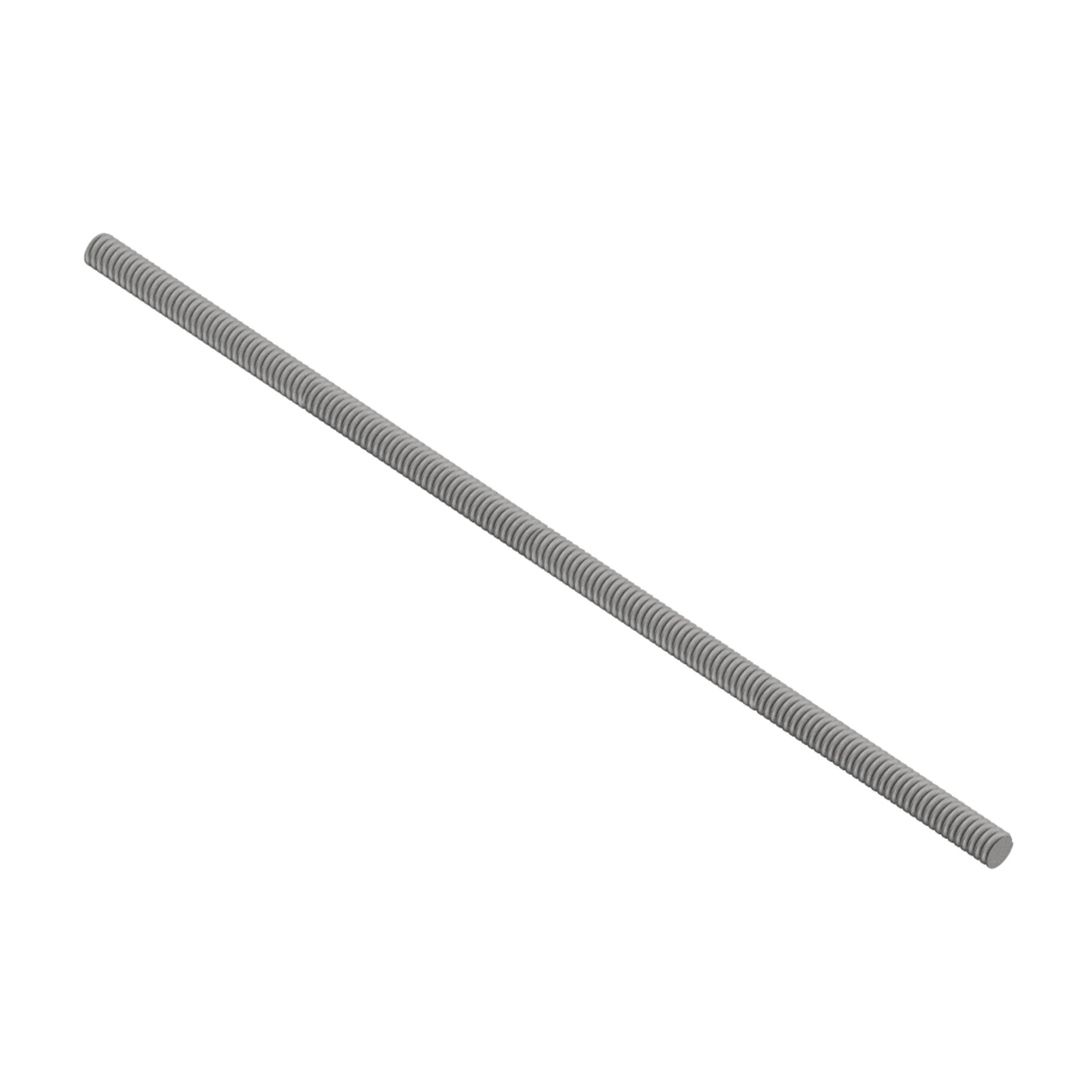
 AG270
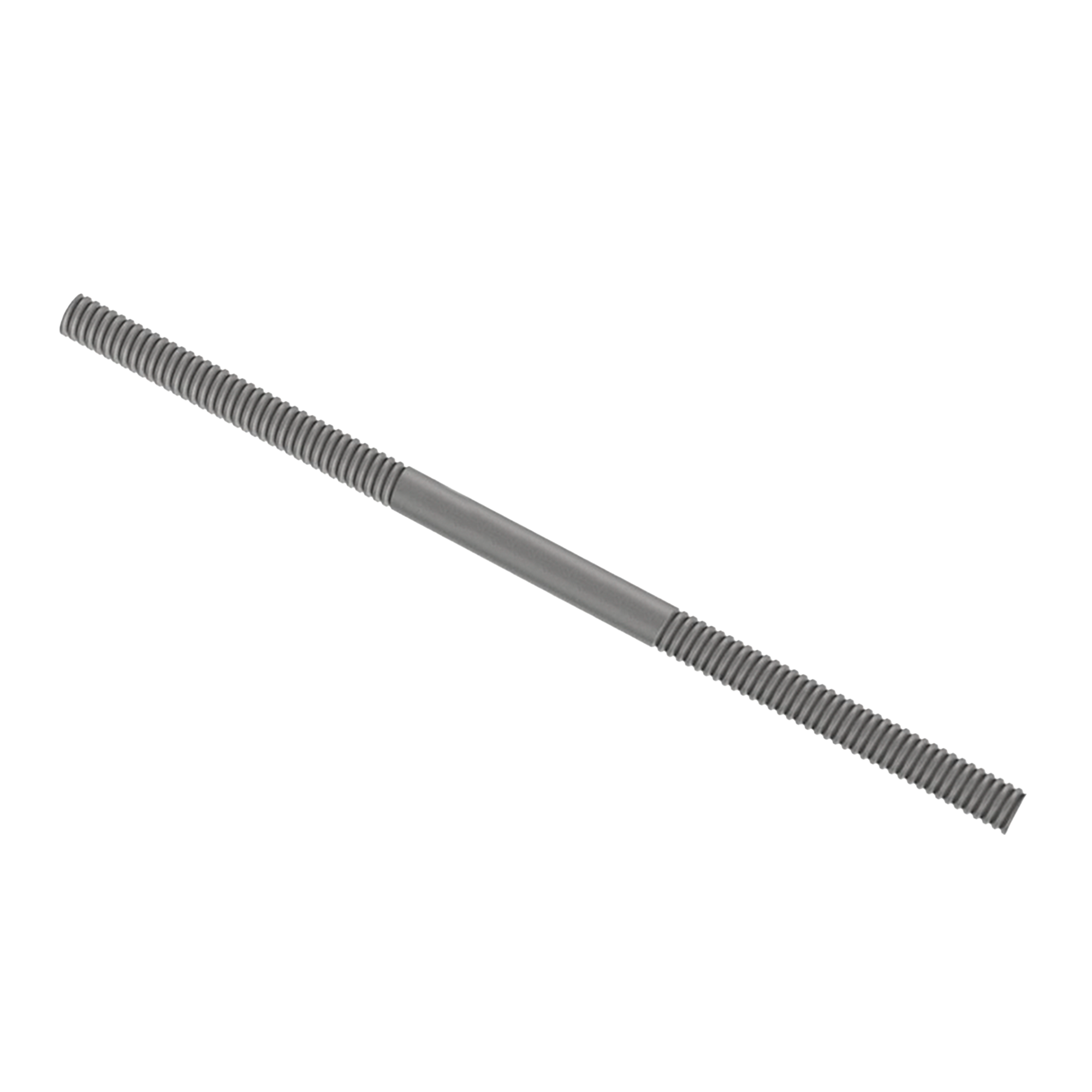
AG270FULLY THREADED ROD
 AG280
AG280DROP ROD RH/LH
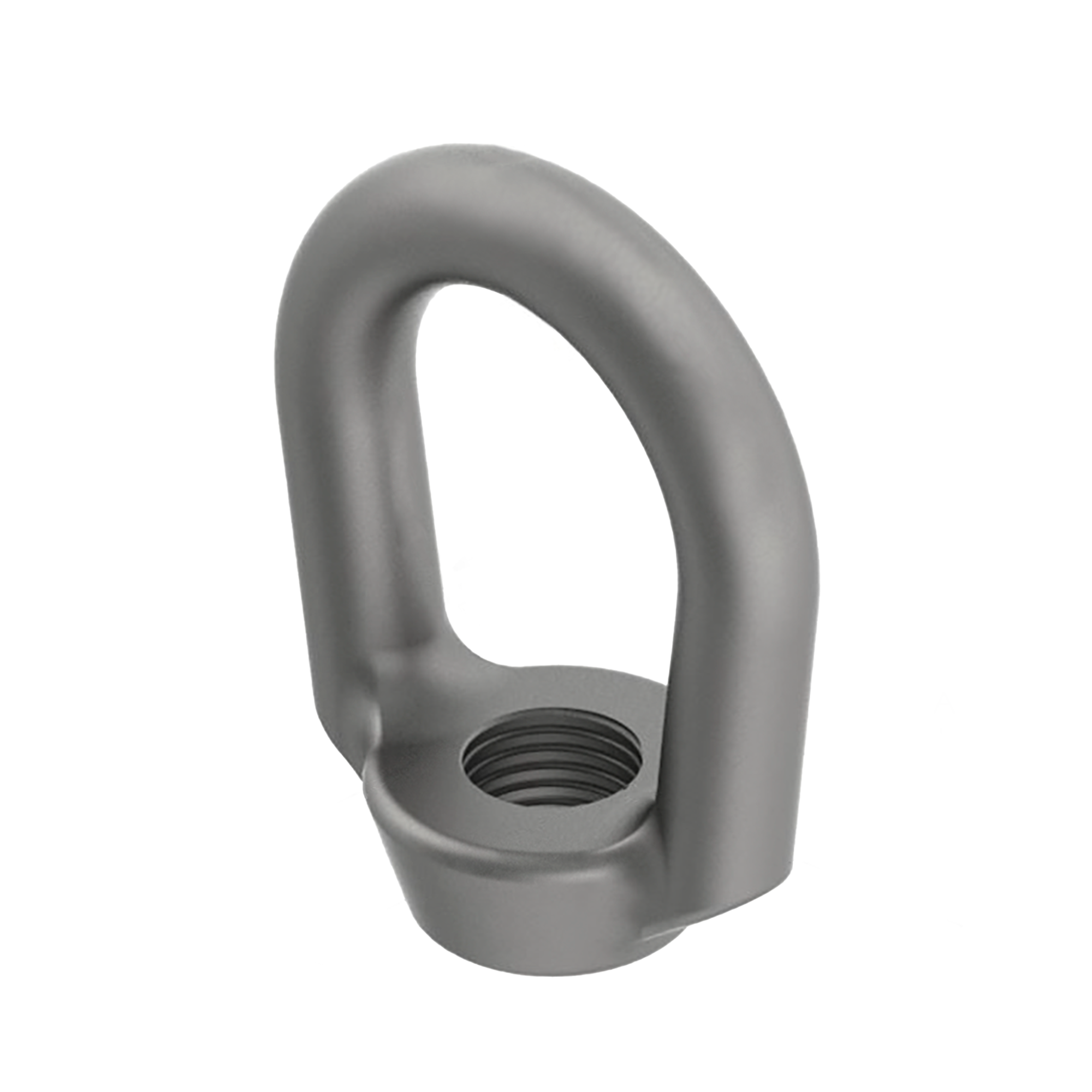
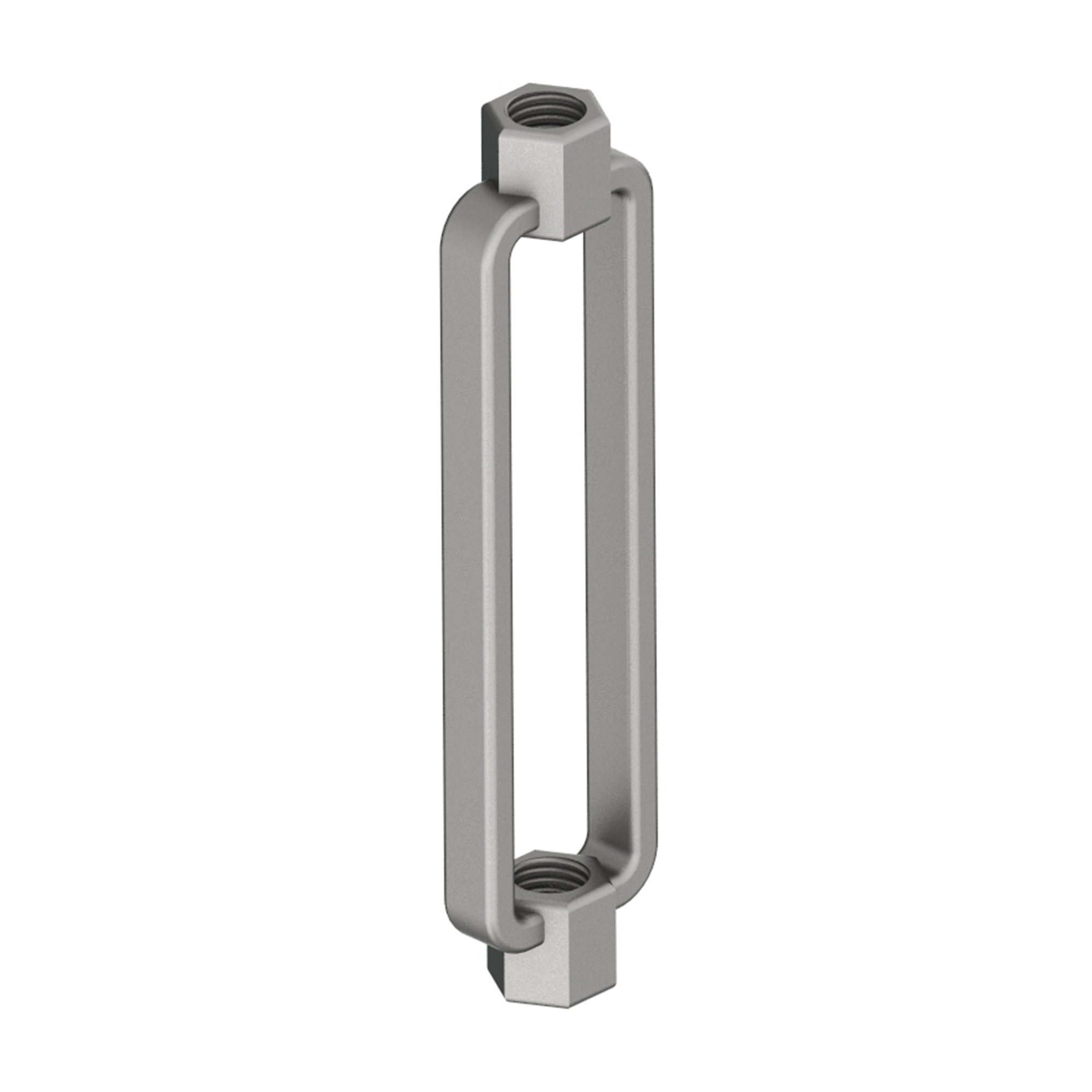
 AG290
AG290FORGED EYE NUT WELDLESS
 AG295
AG295SPADE NUT
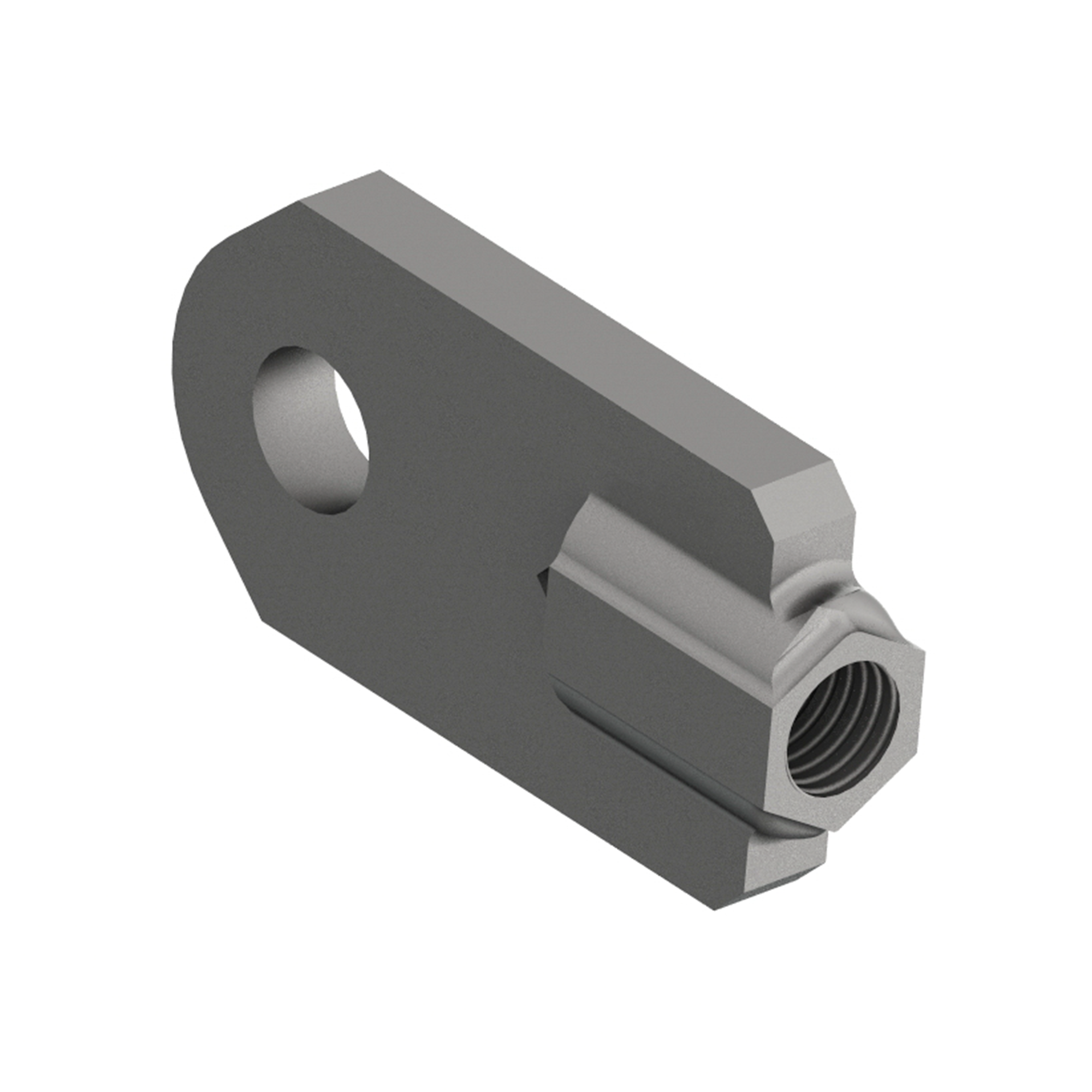
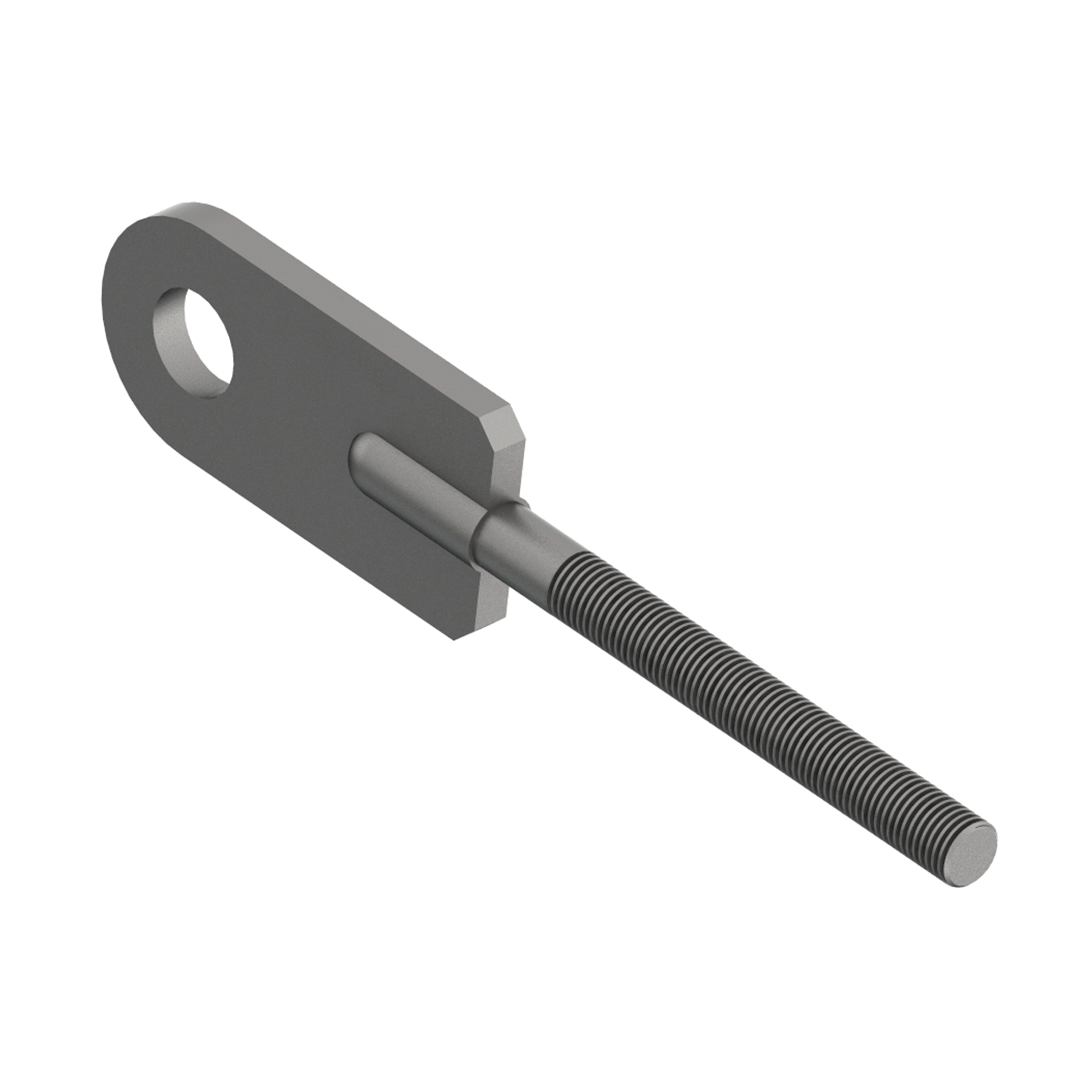
 AG300
AG300SPADE END WITH ROD
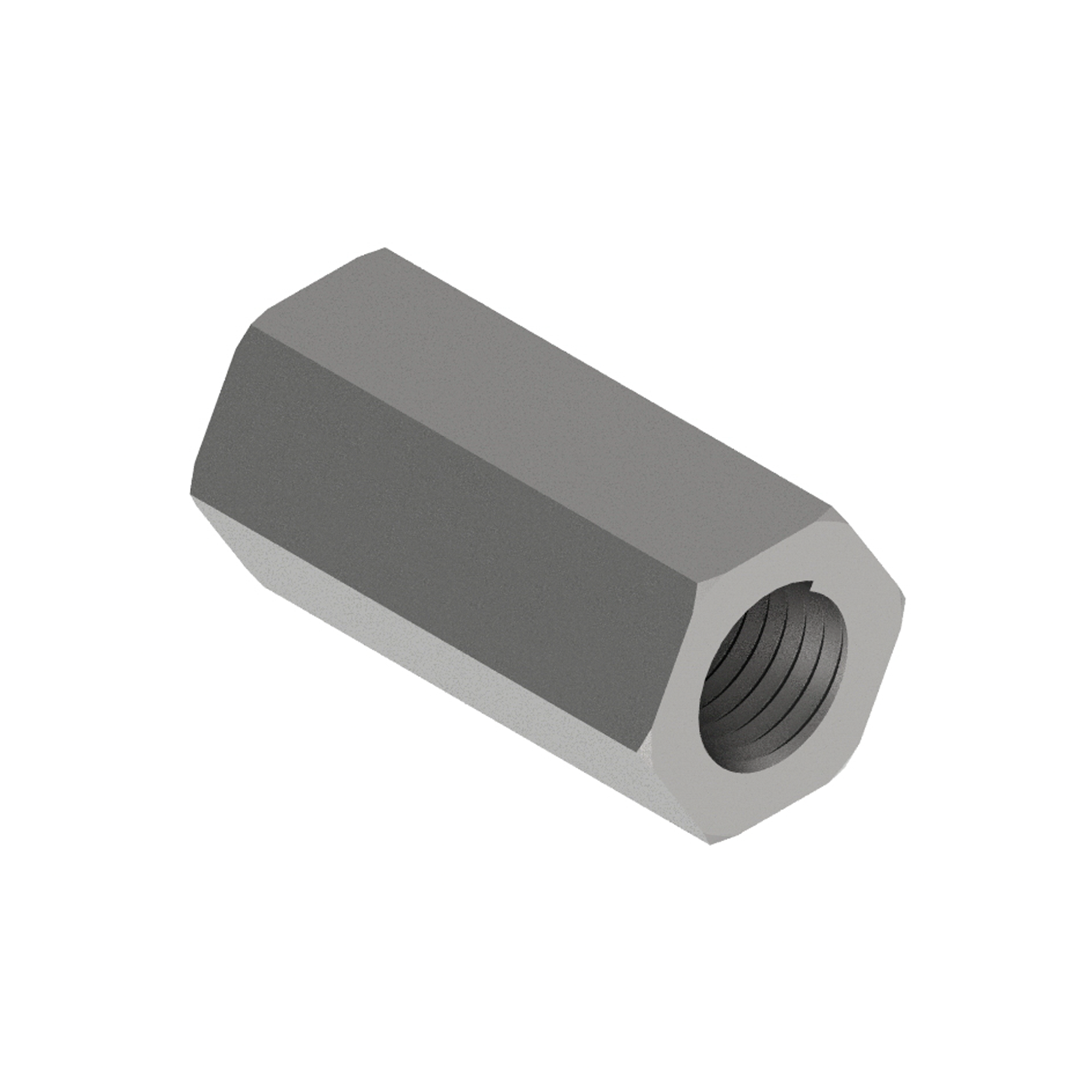
 AG310
AG310HEX CONNECTOR / COUPLER NUT
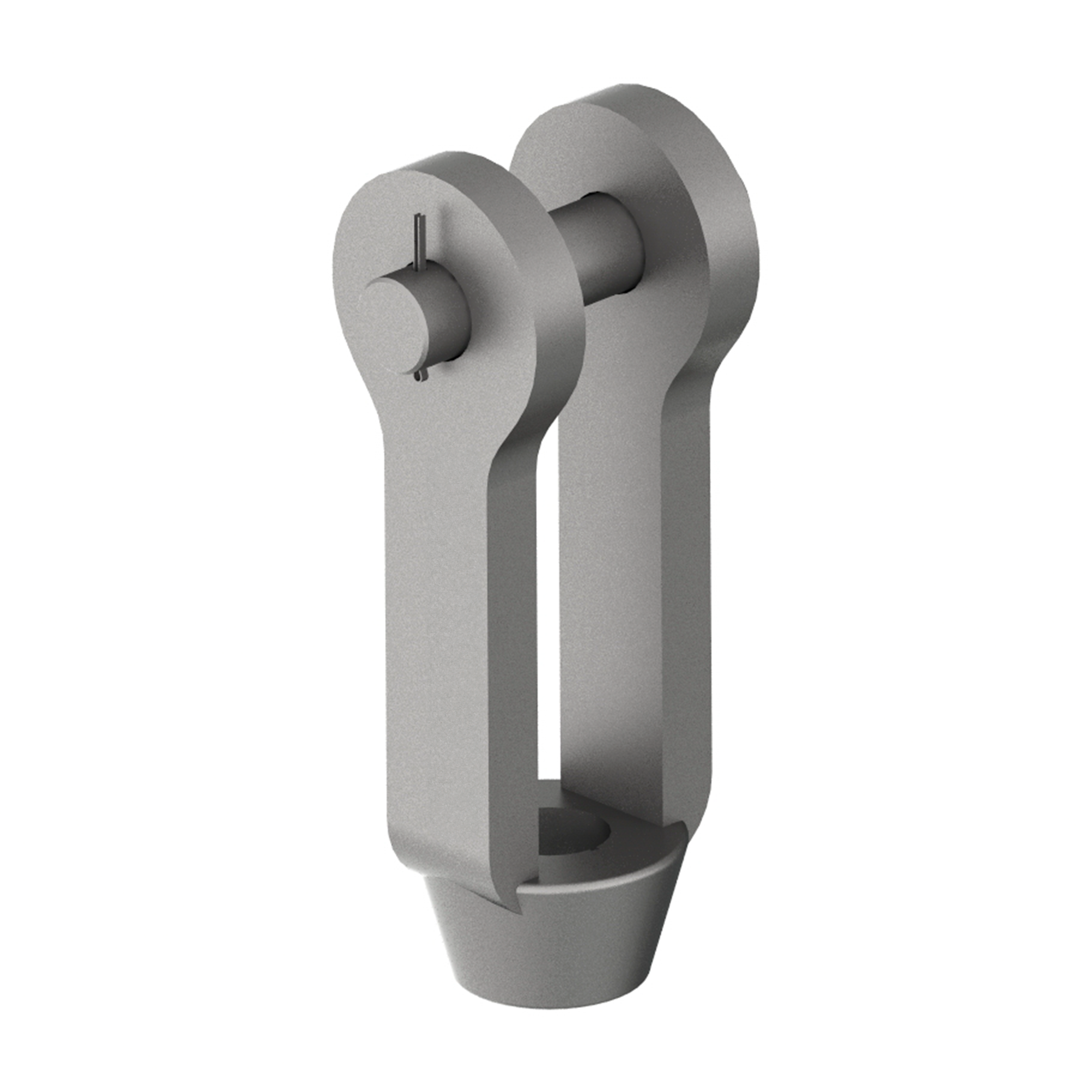
 AG320
AG320FORGED CLEVIS & PIN
 AG330
AG330FORGED TURNBUCKLE
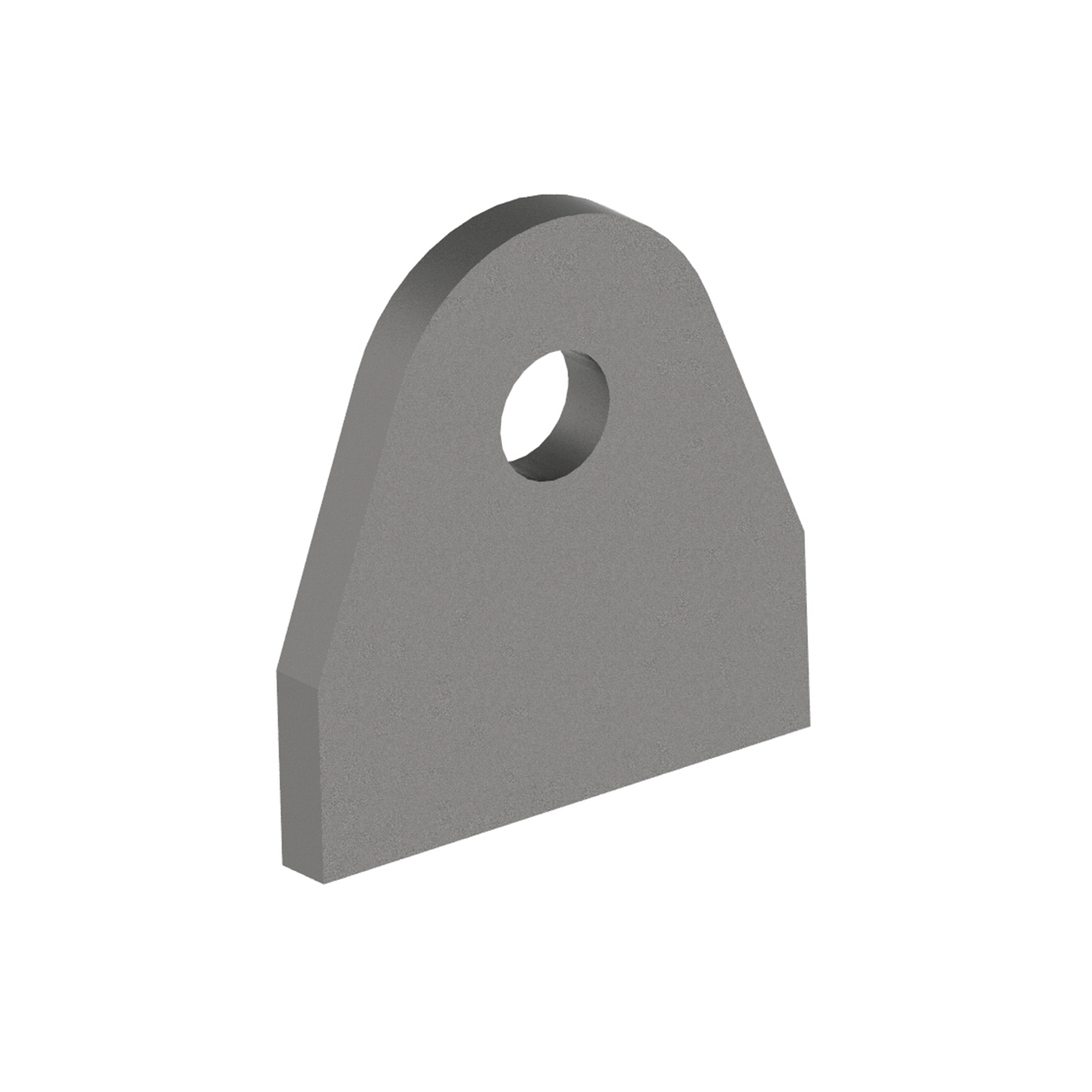
 AG340
AG340PIPE LUG
 AG350
AG350WELDED LUG
 AG360
AG360WELDED BEAM ATTACHMENT
 AG370
AG370WELDED BEAM ATTACHMENT WITH LOAD PIN
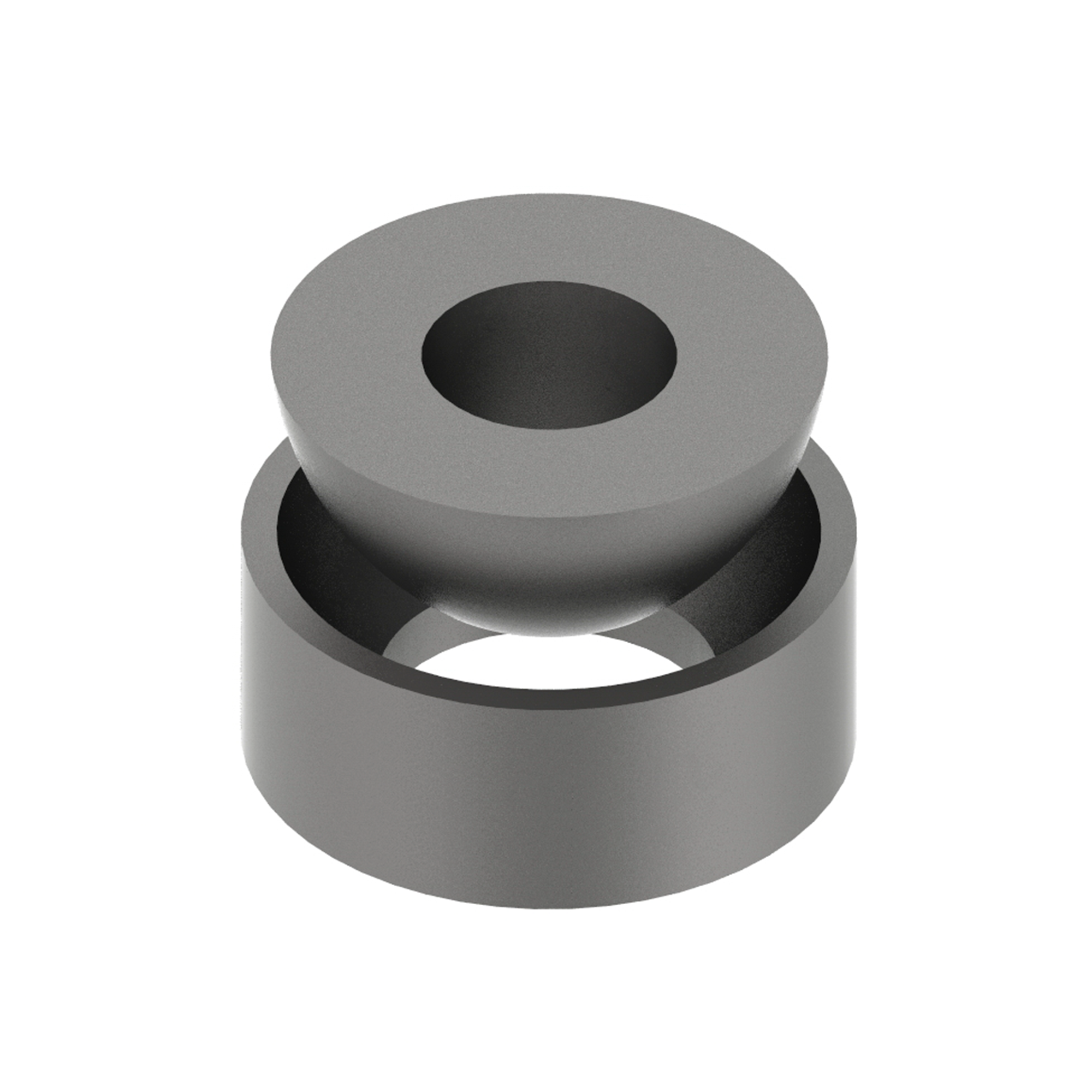
 AG385
AG385HEMISPHERICAL CUP & WASHER
Coming Soon!
-
-
-
- About
- Projects
- Resources
- Contact